Stator pumps, commonly found in various industrial applications, play a vital role in the efficient transport of fluids. These positive displacement pumps use a unique design to handle a wide range of viscous fluids, slurries, and even hazardous materials. One essential aspect of understanding stator pumps is the stator pump diagram, which provides a visual representation of the pump’s components and their functions.
Overview of Stator Pumps
Stator pumps are characterized by their helical rotor and elastomeric stator configuration. This design allows for a smooth and continuous flow, making them ideal for applications such as wastewater management, food processing, and chemical transport. By using a patented helical design, stator pumps minimize pulsation and maintain a consistent flow rate, which is crucial in many industrial processes.
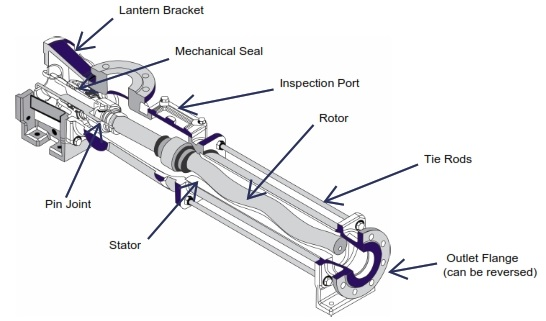
Key Components of a Stator Pump
- Helical Rotor:
The helical rotor is the primary moving part of the pump, designed to create suction and push the fluid through the system. Its helical shape allows for efficient fluid movement with minimal turbulence, making it effective for both thin and thick liquids. - Elastomeric Stator:
Surrounding the rotor, the elastomeric stator forms a cavity through which the rotor moves. The stator’s material can vary based on the application, providing different levels of chemical resistance and flexibility. This flexibility allows the stator to maintain a tight seal against the rotor, preventing leaks and ensuring efficient pumping. - Suction and Discharge Ports:
These ports connect the pump to the piping system. The suction port draws the fluid into the pump, while the discharge port releases it at the required pressure. Proper sealing at these ports is crucial to prevent fluid loss and maintain efficiency. - Frame and Base:
The frame supports the entire pump assembly, ensuring stability during operation. A robust base helps absorb vibrations and maintain alignment, which is critical for the longevity of the pump. - Motor:
Stator pumps can be powered by various types of motors, including electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic systems. The choice of motor directly impacts the pump’s performance and energy efficiency. - Gearbox:
In some stator pump designs, a gearbox is used to adjust the speed and torque delivered to the rotor. This feature allows operators to customize the performance of the pump depending on the fluid’s viscosity and the required flow rate. - Seals and Bearings:
Seals are essential for preventing leaks around the rotor and stator, especially when handling corrosive or hazardous materials. Bearings support the rotor’s movement, reducing friction and ensuring smooth operation.
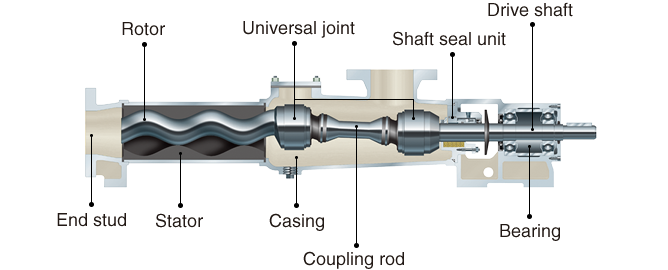
The Importance of the Stator Pump Diagram
A stator pump diagram serves as a crucial tool for understanding how these components interact within the pump. It visually represents each part’s location and function, helping technicians and engineers identify issues and perform maintenance more effectively.
When studying the stator pump diagram, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the labels indicating the various components, their specifications, and their roles in the pumping process. This knowledge is invaluable when troubleshooting or sourcing replacement parts, as it enables quick and accurate identification of the necessary components.
Maintenance and Best Practices
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of stator pumps, regular maintenance is essential. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Inspect the Rotor and Stator: Regularly check these components for signs of wear. The elastomeric stator, in particular, may degrade over time and require replacement.
- Monitor Seals: Inspect seals for leaks, which can indicate wear or improper installation. Early detection of leaks can prevent more severe issues down the line.
- Lubricate Bearings: Proper lubrication is crucial to reduce friction and prevent overheating of the bearings. This maintenance step can significantly extend their lifespan.
- Check Alignment: Ensure that the motor and any attached gearbox are correctly aligned. Misalignment can lead to excessive wear and potential failure of the pump.
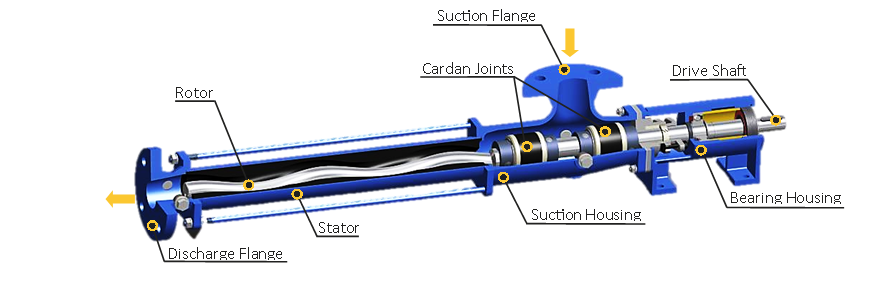
Conclusion
Stator pumps are essential in various industries due to their unique design and versatility. Understanding how they work and the importance of the stator pump diagram can significantly improve operational efficiency and maintenance practices. By familiarizing yourself with the components and maintaining them diligently, you can ensure that your stator pump functions effectively, whether in crude oil transport, wastewater management, or food processing. This knowledge not only enhances performance but also saves time and costs associated with repairs and replacements.