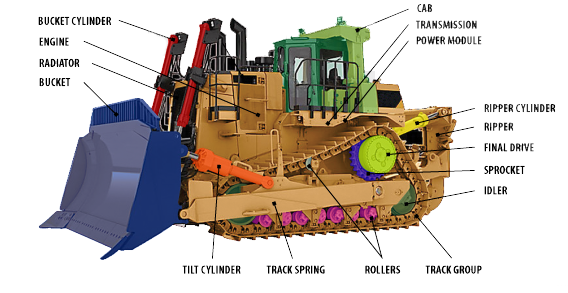
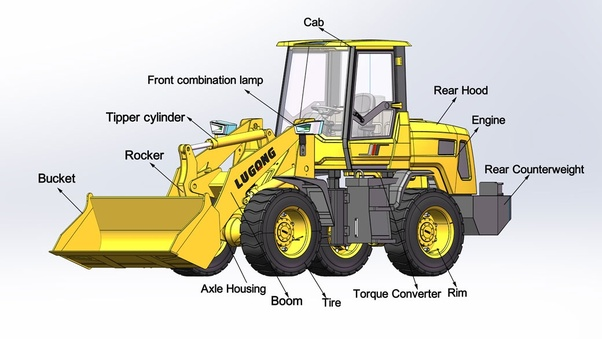
Bulldozers are robust, heavy-duty machines commonly used in construction, mining, and land clearing operations. Understanding the various parts of a bulldozer and their functions is essential for operators, technicians, and enthusiasts to comprehend how these powerful machines operate effectively. Let’s delve into the key parts of a bulldozer and their respective functions:
parts of bulldozer and their functions
- Blade:
The blade, also known as the dozer blade or blade attachment, is the primary tool on a bulldozer used for pushing, lifting, and moving materials such as soil, debris, or rocks. The blade can be angled, tilted, or raised to perform different tasks, such as leveling, grading, or pushing materials. - Cabin:
The cabin serves as the operator’s control center on the bulldozer. It houses the operator’s seat, controls (steering levers, pedals), instrumentation panel, and windows for visibility. The cabin provides a comfortable and safe environment for the operator to oversee operations. - Engine Compartment:
The engine compartment houses the bulldozer’s power source, typically a diesel engine. It includes components like the engine, fuel tank, air filter, cooling system, and exhaust system. The engine provides the necessary power to drive the bulldozer’s tracks and operate hydraulic systems. - Tracks:
Bulldozers are equipped with tracks rather than wheels for increased traction and stability on challenging terrains. The tracks consist of track links, track shoes, rollers, idlers, and sprockets. They enable the bulldozer to navigate rough surfaces, such as mud, rocks, or soft soil, with ease. - Ripper:
The ripper is a specialized attachment located at the rear of the bulldozer used for breaking up hard or compacted materials. It consists of a single or multiple shanks that penetrate the ground and loosen soil, rock, or asphalt before the blade pushes or grades the material. - Hydraulic System:
The hydraulic system in a bulldozer powers the blade, ripper, and other attachments. It consists of hydraulic pumps, cylinders, hoses, and control valves. The hydraulic system enables the operator to control the movement and functions of the blade and other hydraulic components. - Undercarriage:
The undercarriage supports the weight of the bulldozer and provides stability and mobility. It includes components like tracks, rollers, idlers, and sprockets. The undercarriage allows the bulldozer to move smoothly across various terrains and withstand heavy loads during operation. - Counterweight:
Some bulldozers feature a counterweight at the rear of the machine to enhance stability and balance when lifting or pushing heavy loads with the blade. The counterweight helps prevent tipping and ensures safe operation in challenging conditions.
Understanding the parts of a bulldozer and their functions is crucial for operating the machine efficiently, maintaining its performance, and ensuring safety on the job site. Regular maintenance, inspections, and adherence to safety protocols are essential for maximizing the productivity and longevity of bulldozers in demanding work environments. Each part plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the bulldozer, making it an indispensable asset in earthmoving and construction operations.